Air pollution is a critical global concern that affects both human health and the environment. Total Suspended Particulate (TSP) is one of the significant components of air pollution, encompassing tiny solid particles and liquid droplets suspended in the air. Measuring TSP is essential in understanding the quality of the air we breathe and taking necessary actions to protect public health and the environment. Keep reading the post, and learn more about TSP.
What Is TSP?
TSP consists of various particles, including dust, soot, smoke, and aerosols. These particles are small enough to remain suspended in the air for extended periods. TSP particles range in size from coarse to fine, and some can be breathed deep into the lungs, causing serious health problems.
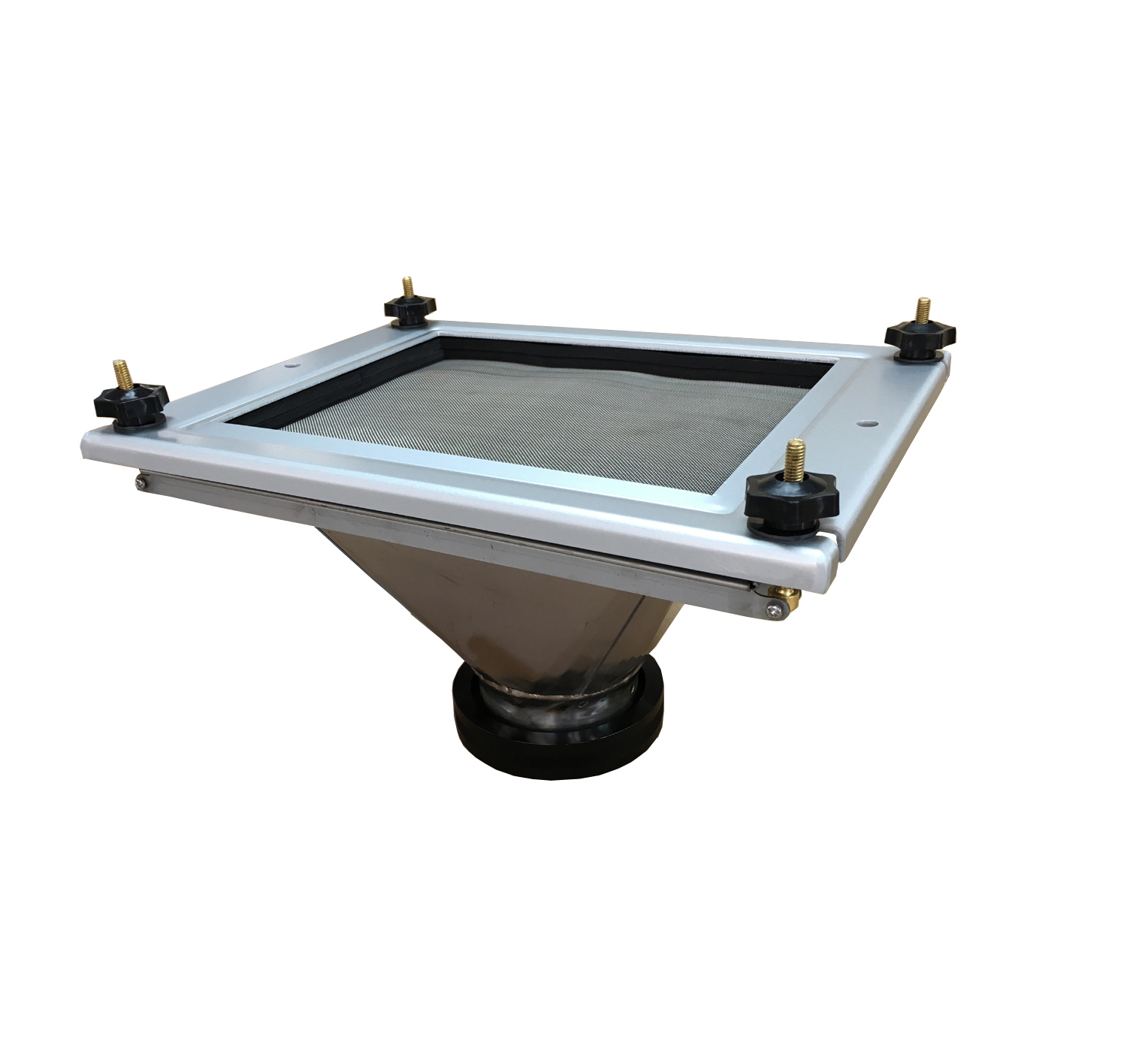
Importance Of Measuring TSP
Here are two major importance of measuring TSP:
Impact On Human Health
Measuring TSP levels is essential to understand its impact on human health. People who are exposed to high levels of TSP, particularly PM10, and PM2.5, are at risk of having respiratory disorders, cardiovascular ailments, and other health issues. Children, the elderly, and individuals with pre-existing respiratory conditions are particularly vulnerable to the adverse effects of TSP exposure.
TSP Monitoring In Industrial Settings
Industries are significant contributors to TSP emissions, releasing various particulates into the atmosphere during manufacturing and production processes. TSP levels in industrial settings must be monitored to detect potential sources of emissions and assure compliance with environmental requirements.
By analyzing TSP data from industrial sites, companies can implement effective pollution control strategies. These may include installing emission control technologies, optimizing production processes, and adopting cleaner and more sustainable practices.
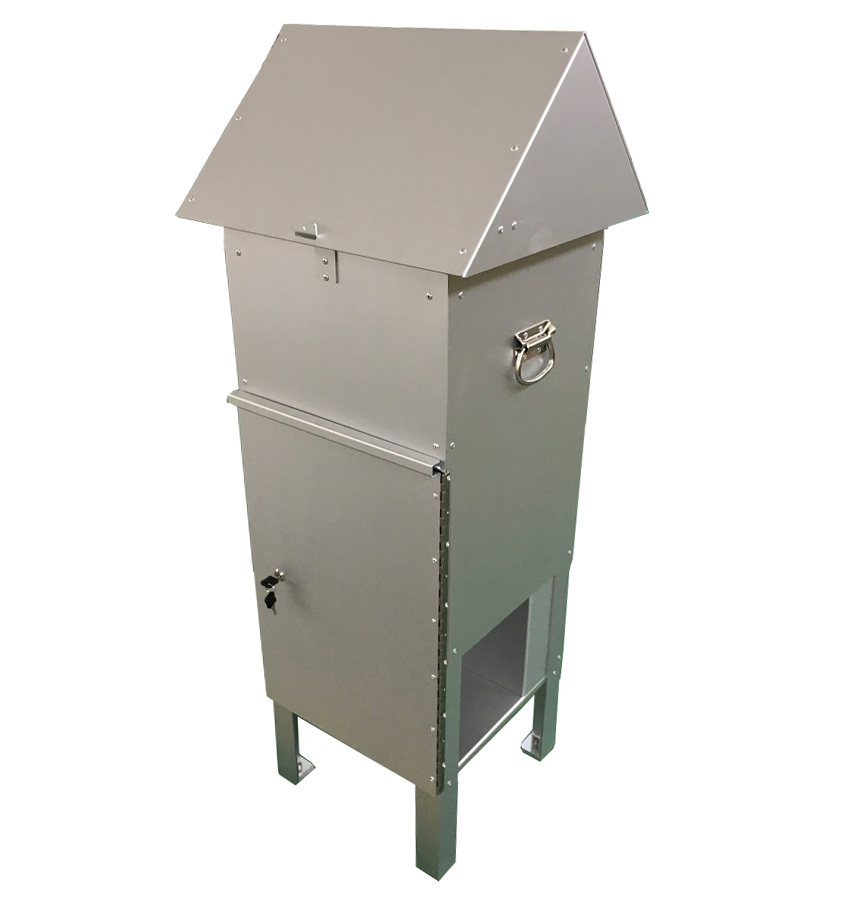

How To measure TSP?
Here are some methods of measuring TSP:
Gravimetric Method
The gravimetric method is a widely used technique to measure TSP levels. It involves collecting air samples on filters, which capture the suspended particles. The filters are carefully weighed after a specific sample interval to ascertain the mass of TSP collected. This approach yields accurate data and is frequently used as a benchmark for other measuring techniques.
Beta Attenuation Monitor (BAM)
The Beta Attenuation Monitor (BAM) is an automated monitoring system used to measure TSP in real-time. It employs a beta radiation source and detectors to gauge the amount of beta radiation attenuated by the TSP-laden filters. BAM data offers continuous, immediate observations, enabling for quick reactions to abrupt surges in TSP levels.
Tapered Element Oscillating Microbalance (TEOM)
The Tapered Element Oscillating Microbalance (TEOM) is another popular method for measuring TSP concentrations. It utilizes a filter element that oscillates within a flow of ambient air. The oscillation frequency changes as TSP particles accumulate on the filter. The mass of TSP collected may be calculated in real-time by monitoring these frequency variations.
Environmental Impact
TSP also has significant implications for the environment. When these particles settle, they can deposit on soil, water bodies, and vegetation, affecting ecosystems and wildlife. TSP deposition can harm crop output and soil quality in agricultural regions. Furthermore, TSP leads to the creation of smog and acid rain, deteriorating air and water quality even further.
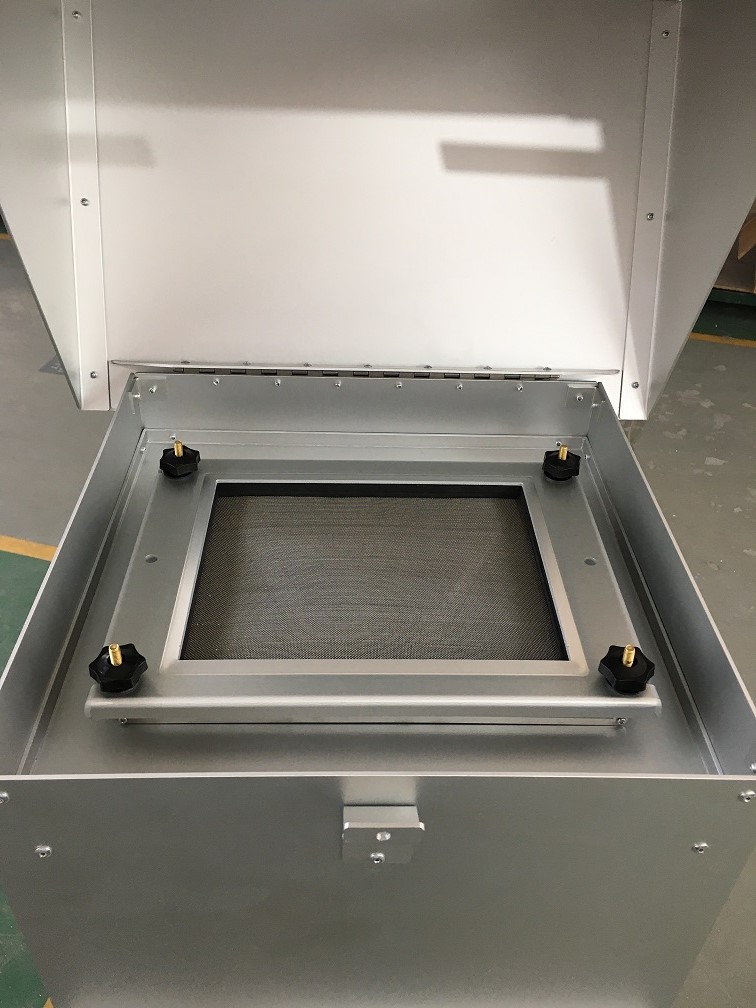
Addressing High TSP Levels
When TSP levels exceed recommended limits, it is essential to take immediate action to protect public health and the environment. Addressing high TSP levels involves a multi-faceted approach:
Source Identification
Identifying the sources of TSP emissions is critical for developing effective pollution control strategies. Source apportionment studies use advanced modeling techniques and measurement data to determine the contributions of different pollution sources.
Mitigation Strategies
Implementing mitigation strategies is key to reducing TSP levels and improving air quality. Such strategies may include:
Emission Control Technologies: Industries and vehicles can adopt technologies that capture and reduce particulate emissions, such as filters and catalytic converters.
Alternative Fuels: Encouraging the use of cleaner fuels like natural gas or electricity in transportation and industry can help reduce TSP emissions.
Urban Planning: Well-designed urban planning, with a focus on reducing traffic congestion and promoting green spaces, can help mitigate TSP levels in cities.
Regulatory Measures: Strengthening and enforcing regulations on industrial emissions and vehicle standards can lead to substantial reductions in TSP pollution.
Conclusion
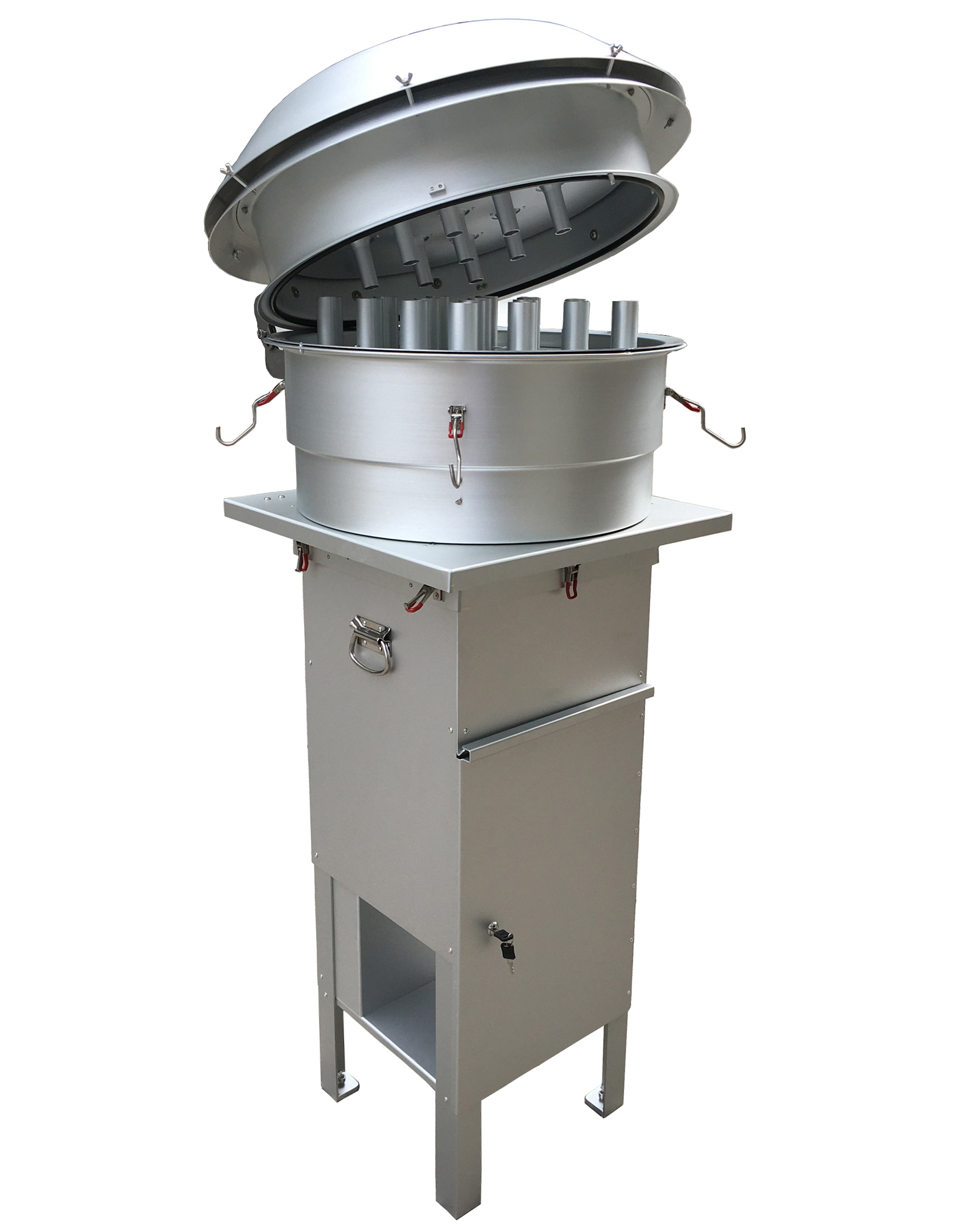
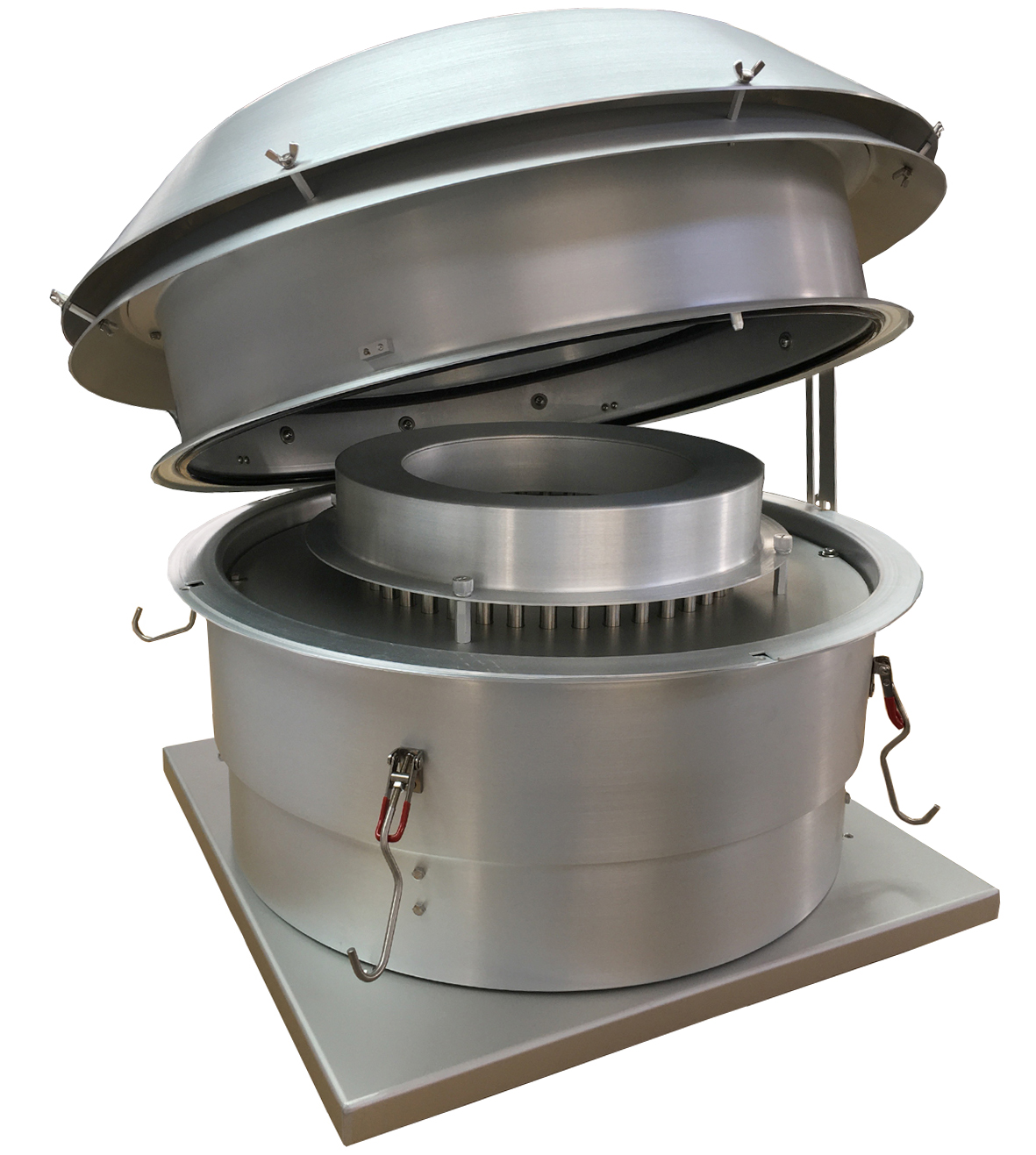
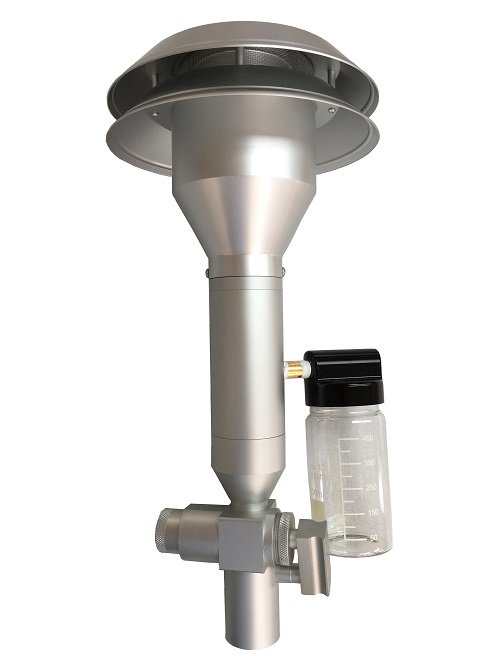
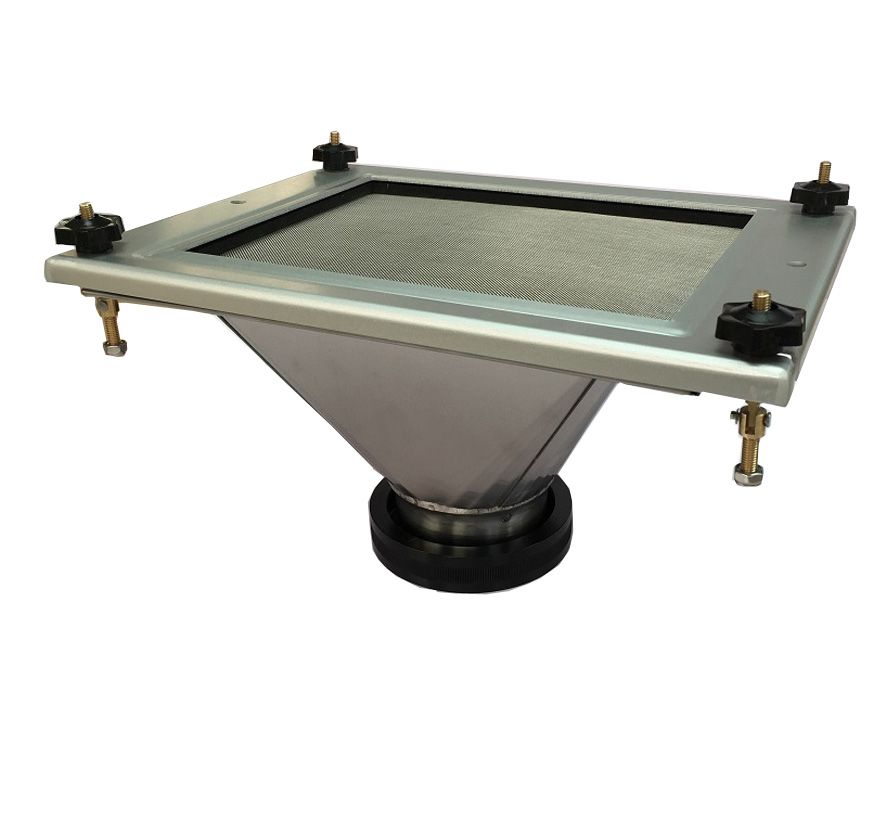
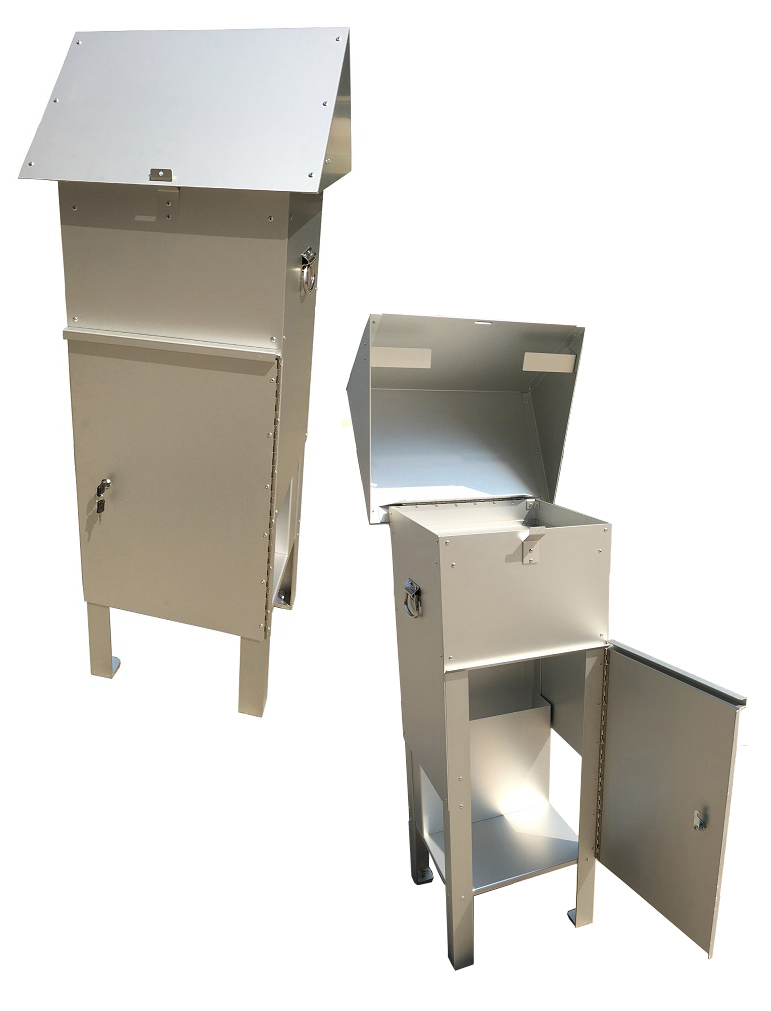
Measuring Total Suspended Particulate (TSP) is of utmost importance in understanding the impact of air pollution on both human health and the environment. If you are looking for a high-quality TSP Filter Holder and TSP Cabinet, T4 AIR SAMPLER is ideal for you. We offer a wide range of filters including PM 2.5 and PM10 filters. Browse our website for more product details!



.jpg)



